New Entries in the CFR Cyber Operations Tracker: Q2 2020
An update of the Council on Foreign Relations’ Cyber Operations Tracker for the period between April and June 2020.
By experts and staff
- Published
Experts
![]() By Adam SegalIra A. Lipman Chair in Emerging Technologies and National Security and Director of the Digital and Cyberspace Policy Program
By Adam SegalIra A. Lipman Chair in Emerging Technologies and National Security and Director of the Digital and Cyberspace Policy Program
This blog post was coauthored by Connor Fairman, research associate for the Digital and Cyberspace Policy program.
Corbin Stevens, Digital and Cyberspace Policy program intern, oversaw data collection for new entries.
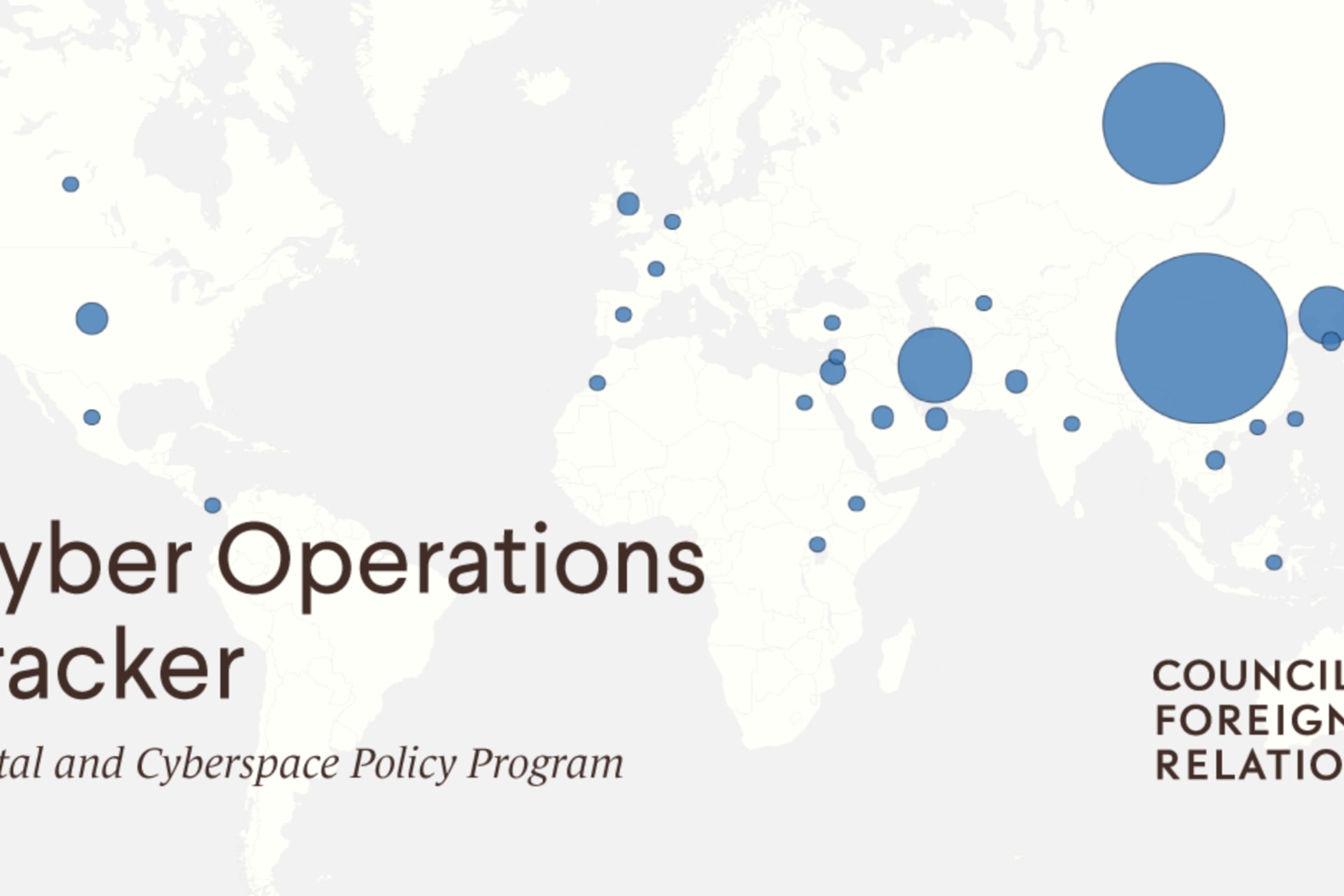
The Cyber Operations Tracker has just been updated. This update includes the state-sponsored incidents and threat actors that have been made public between April 2020 and June 2020. We also modified some older entries to reflect the latest developments.
Here are some highlights:
- The Cyber Operations Tracker has an updated design with an interactive map showing the origins of state-sponsored cyber operations as well as by victim type. Click here to view the map.
- Suspected Vietnamese threat actor Ocean Lotus sent spear-phishing emails to officials from the Wuhan city government and China’s Ministry of Emergency Management and also uploaded malware-infected apps to the Google Play store to trick users into downloading them onto their phones.
- Hackers associated with the Iranian government sought to cripple computers that control water flow and wastewater treatment for two rural districts in Israel. In retaliation, Israel launched a cyberattack against Iran’s Shahid Rajaee Port, disrupting its operations. This is the first documented instance of a state confirming it used cyber means against another state in retaliation for a cyber operation.
- Suspected North Korean-affiliated threat actor Hidden Cobra used a variety of malware tools to hack into and steal money from banks, cryptocurrency exchanges, and ATMs.
A detailed log of the added and modified entries follows. If you know of any state-sponsored cyber incidents that should be included, you can submit them to us here.
Edits to Old Entries
Stolen data on nearly two thousand Mitsubishi employees. Included disclosure that the breach resulted in the theft of specifications for a hypersonic missile that Japan had been developing.
Compromise of the networks at the German parliament (Bundestag). Added details regarding Germany’s arrest warrant issued against Dmitry Badin and request that European Union governments impose cyber sanctions against him.
New Entries
Syrian Electronic Army (4/15)
Pirate Panda (4/30)
Greenbug (5/19)
