No Helping Hand: Federal Worker-Retraining Policy
Progress Report and Scorecard

BY
- Robert Maxim
Overview
How America Stacks Up: Economic Competitiveness and U.S. Policy compiles all eight Progress Reports and Scorecards from CFR’s Renewing America initiative in a single digital collection. Explore the book and download an enhanced ebook for your preferred device.
A decade ago the United States had the lowest share of long-term unemployed workers among developed nations. But today U.S. long-term unemployment levels are nearly as high as those in Europe, despite stronger overall U.S. economic performance. In 2000, 11.4 percent of unemployed American workers had been out of work for more than six months, compared to 51.9 percent in the rest of the Group of Seven (G7) countries. Throughout the recession those numbers were converging. In 2013, 37.6 percent of unemployed workers in the United States had been out of work for more than six months; that rate was 53.8 percent in the rest of the G7.
U.S. federal employment and training programs that assist job seekers do little to help the long-term unemployed prepare for different careers.
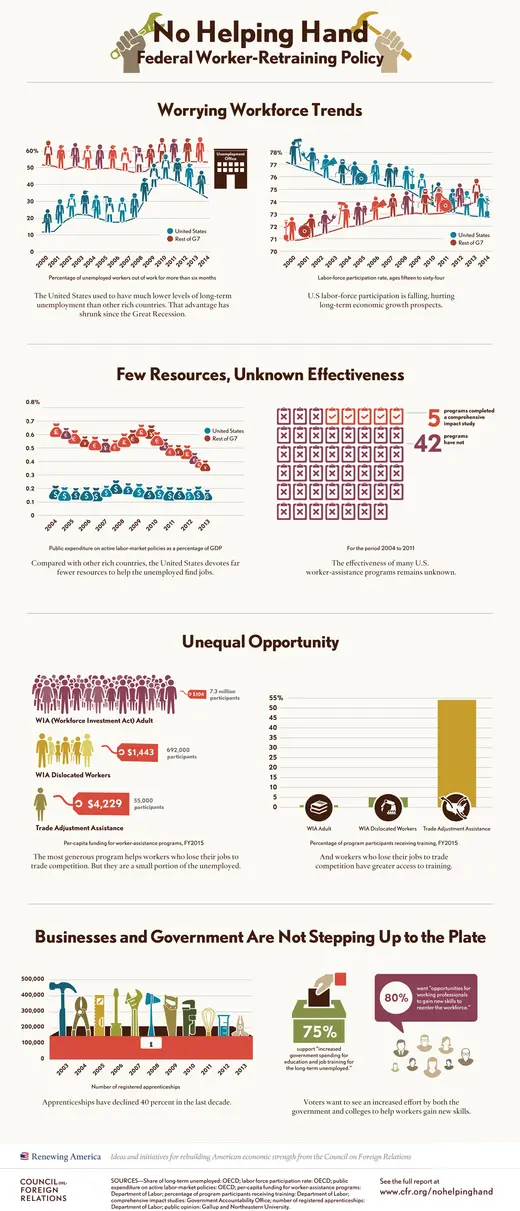
“Ineffective worker-adjustment policies undermine economic recovery, lead to skills shortages for employers, and hurt U.S. competitiveness,” Research Associate Robert Maxim explains in the progress report. “Other advanced economies invest more in worker adjustment and use innovative programs to minimize unemployment.”
The United States spends far less on programs that directly help people find work than other developed countries do, in part because past U.S. unemployment was mostly short-term, and the unemployed tended to be rehired for similar jobs. In 2011, the most recent year for which comparable data is available, the rest of the G7 spent five times as much on active labor market measures as the United States did. Nations with a lengthier history of long-term unemployment, such as Germany and Denmark, have taken a more proactive role in equipping the unemployed with new skills and identifying available jobs.
Although the United States has nearly fifty employment and training programs across nine federal agencies, this system fails to provide adequate assistance for most eligible Americans, and allocates its limited resources unequally among the unemployed. During a recent five-year period the Government Accountability Office found that only five of these programs had undergone impact studies to determine whether workers’ success could be attributed to the programs.
Congress has shown some willingness to work across the aisle on jobs. A compromise bill, the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act, passed the previous Congress with bipartisan support in July 2014. But the bill leaves the existing system largely intact, and more innovative approaches are still needed.
This scorecard is part of CFR’s Renewing America initiative, which generates innovative policy recommendations on revitalizing the U.S. economy and replenishing the sources of American power abroad. Scorecards provide analysis and infographics assessing policy developments and U.S. performance in such areas as infrastructure, education, international trade, and government deficits. The initiative is supported in part by a generous grant from the Bernard and Irene Schwartz Foundation.
Download the scorecard [PDF].
Table of Contents
Click on a chapter title below to view and download each Progress Report and Scorecard.t






